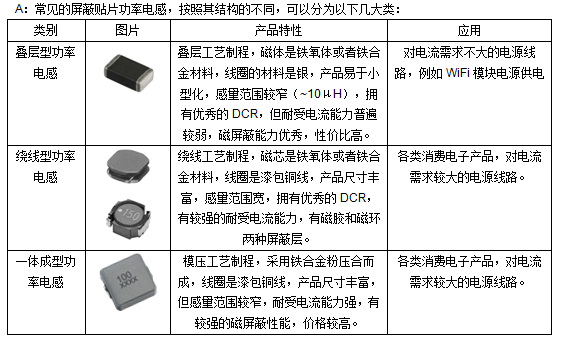
Thermistors are a kind of sensitive elements, which can be divided into positive temperature coefficient thermistors (PTC) and negative temperature coefficient thermistors (NTC) according to different temperature coefficients. The typical characteristic of thermistors is that they are sensitive to temperature and show different resistance values at different temperatures. Positive temperature coefficient thermistor (PTC) has a higher resistance value at higher temperature, while negative temperature coefficient thermistor (NTC) has a lower resistance value at higher temperature. According to different materials, PTC can be divided into ceramic PTC thermistor (CPTC) and polymer PTC thermistor (PPTC). The differences between these types of thermistors are shown in the following table:
| category | CPTC | PPTC | Temperature sensing NTC | Power NTC |
| mechanism | Nonlinear PTC effect (abrupt/step) | Electron level transition | ||
| Material Science | PTC effect is formed by doping semiconducting elements into BaTiO3, V2O5, BN and other materials | Formation of PTC Effect by Adding Carbon Black into Polyethylene Polymers | Manganese, cobalt, nickel, copper and other metal oxides are the main materials | |
| Zero power resistance | Generally more than 1 Ω, with large loss on the road | A few m Ω~a few Ω, low on road loss | Class K Ω | Grade Ω |
| electric current | Inactive current mA level, applicable to small current protection | Inactive current class A, applicable to large current protection | Avoid temperature rise caused by self heating and affect temperature measurement. The maximum allowable working current is mA | Maximum steady state current Class A |
| Tolerance | High voltage and large current impulse withstand capability is good, and the maximum working voltage is 1KV | It is not resistant to high voltage and large current impact, and the maximum working voltage is 600V | Do not withstand high voltage and large current impact, | Withstand high current impact, not high voltage impact |
| Action state | The action time is relatively slow (hundreds of ms), the recovery time is long, and the recoverability and stability are good after the action | The action speed is fast (several ms), the recovery time is short, and the resistance value cannot be restored to the original value after the action | Very sensitive to temperature, with rapid thermal response | The initial resistance can restrain the transient current in the line. The current increases the temperature of the porcelain body, and the resistance value decreases exponentially. The residual resistance is only m Ω, which has little impact on the overall line |
| effect | Overcurrent protection, overheat protection, motor startup, delayed startup, heating, demagnetization, etc | Overcurrent protection | Temperature measurement, temperature compensation, temperature protection | Suppress transient surge current when starting |
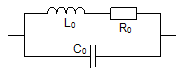
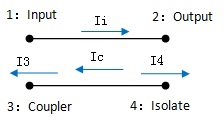
Coupling=10log (P3/P1)
DBm is a value representing the absolute value of power (it can also be considered as a ratio based on 1mW power), and the calculation formula is 10log (power value/1mw).
If the power P is 1mw, it will be 0dBm after being converted into dBm.
For a power of 40W, the converted value in dBm units shall be:
10log(40W/1mw)=10log(40000)=10log4+10log10000=46dBm。